Navigating Neurodivergence Trauma
For therapists, trauma-informed care is of primary focus in our training and treatment. This approach, characterized by sensitivity to trauma and its...
5 min read
 KD & Marielle
:
Jun 29, 2023 4:06:06 PM
KD & Marielle
:
Jun 29, 2023 4:06:06 PM
Trauma is a word that has been gaining more attention and importance in our society and in the therapy treatment world. We (therapists) all know what trauma is... an overwhelming psychological and emotional response to an event or series of events that causes the brain to “push the panic button”. By now we all know trauma can come in many forms. It could be a natural disaster, a car accident, physical abuse, or emotional neglect. But the type of trauma that shows up most often in the therapy room is developmental trauma, which occurs in childhood and has a profound impact on a person's life.
The effects of developmental trauma, if not treated, can last well into adulthood. This is why it is so important that we therapists, understand the biology of the brain and mental health symptoms associated with developmental trauma. Especially important is understanding stabilization skills that are the foundation of treating developmental trauma and can be used at any level of therapist development.
Stabilization skills refer to the ability to manage the present-day emotional dysregulation or numbing that brings our clients to therapy. This emotional dysregulation and numbing is often rooted in their trauma history. A caregiver’s primary job is to model and assist their children in emotion regulation so that they grow up being able to feel, and regulate their emotions. If a parent can’t get their child to calm (because they, themselves are not able to be calm), the child grows up with dysregulated emotions and a heightened sense of alertness. So, the therapeutic focus in building stabilization is often on assisting individuals in coping with their present-day symptoms in order to build a stronger foundation so they can later address the source of the trauma. The goal is to help individuals gain proficiency in regulation of their feelings, thoughts, and behaviors to allow them to achieve a sense of equilibrium. Stabilization skills are essential in helping individuals build resilience, a quality necessary for overcoming the effects of trauma.
A variety of treatment methods are used to treat developmental trauma, but it all starts with stabilization. Once a client is stable emotionally and is somewhat able to manage their triggers and responses, then trauma reprocessing can proceed. These trauma reprocessing methods aim to help individuals with trauma to gain a better understanding of the source of their trauma and process their emotions and thoughts in a healthy and supportive environment. Trauma-focused therapy frameworks such as EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing), DBR (Deep Brain Reorienting) and ImTT (Image Transformation Processing) have shown promising results in the ability to do this for clients.
Complex Trauma, or Complex PTSD (CPTSD), is most often related to experiences of developmental trauma in which an individual’s environment was emotionally unstable or unpredictable. A client has symptoms of PTSD plus symptoms of intense emotion dysregulation, markedly irrational views of the world, dissociation, depersonalization, or derealization symptoms. Individuals with CPTSD are more likely to abuse substances to regulate their consistent states of overwhelm. It is these clients who are most likely to benefit from a thorough implementation of stabilization skills prior to starting any reprocessing therapy or somatic therapy techniques. They are either simply too easily triggered or dysregulated or they are so skilled at “ignoring and forgetting” what happened so going into the trauma material too much too soon can destabilize the client.
Clients that fall under the Neurodivergent umbrella are neurologically diverse (ADHD, Autism, Learning Differences, and many more) and statistically are more likely to be polyvicitimized which means they will have multiple traumatic events throughout their lifetime. These individuals are at risk for CPTSD. Understanding how to meet Neurodivergent needs therapeutically is an integral part of being a trauma informed therapist.
Individuals within the Neurodivergence spectrum may exhibit variations in attention and sensory processing, which play a crucial role in tailoring therapeutic interventions. This concept is well-recognized in the realm of Occupational Therapy, where sensory sensitivities, both hypo and hyper, influence how individuals perceive and respond to stimuli in their surroundings.
In the field of trauma treatment, we understand that individuals with sensitive nervous systems are more susceptible to experiencing heightened trauma responses. Delving deeper into these differences allows us to gain a comprehensive understanding of how these unique sensory and attentional variations impact the way individuals navigate traumatic experiences.
Individuals exhibit a range of sensory variations, some of which may extend to the point of significantly impacting their functioning and having a Sensory Processing Disorder. As therapists, it is our responsibility to discern and pinpoint the factors that influence our clients' overall well-being and functioning.
Understanding sensory differences is crucial in how individuals perceive and interact with the world around them. By incorporating these unique sensory variations into our therapeutic approach, we can provide more effective care for our clients. When addressing trauma, it is essential to consider all aspects of our clients' functioning to develop effective coping strategies.
Treating developmental trauma is essential for a person's overall well-being and future success. It is often a complex and sometimes uncomfortable process, but it is necessary for individuals to achieve effective emotional and behavioral responses. Understanding the biology of the brain, mental health symptoms that accompany trauma, and stabilization skills are paramount in treating trauma. It is important to remember that trauma treatment is a delicate dance, where together we build resilience, and empower our clients to live a fulfilling life.
If you would like to learn more about treating Developmental Trauma, check out our live webinar for any level of professional development; where we (KD Holmes, LPC and Marielle Babb, LPC, and Brynne Angelle, LCSW) will delve into the biology of the brain, dissociation, neurodivergence, stabilization skills, and briefly describe forms of Trauma Treatment.

For therapists, trauma-informed care is of primary focus in our training and treatment. This approach, characterized by sensitivity to trauma and its...
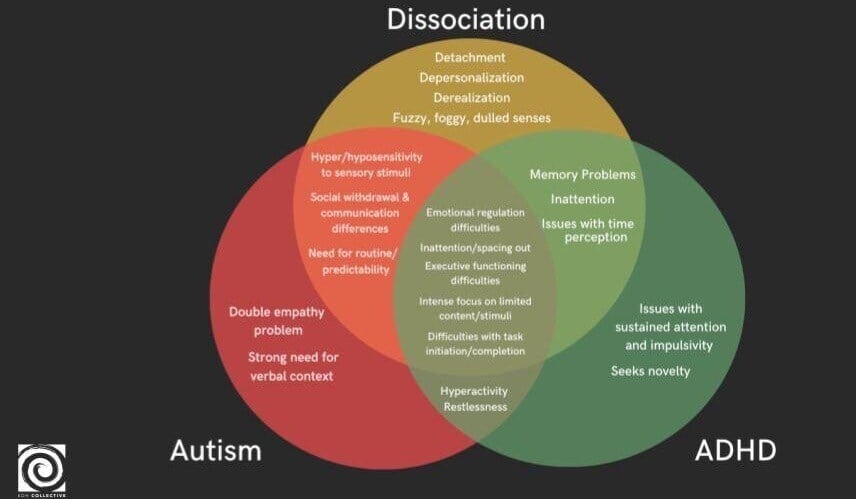
Exploring the complexities of mental health, the threads of neurodivergence and dissociation weave together in intricate patterns. For therapists,...
Trauma-informed therapy explains the connection between the nervous system and mental health, offering a paradigm shift in treating mental health...